ASC 606
The new model’s core principle for revenue recognition is to “depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services.” This principle was established by both the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) and is the underpinning of the entire revenue framework. In particular, it identifies and answers the two most fundamental questions related to revenue.
When may an entity recognize revenue?
The entity may recognize revenue when it satisfies its obligations under a contract by transferring goods or services to its customer. (That is, when the entity performs, it should recognize revenue.)
How much revenue may an entity recognize?
The entity may recognize the amount to which it expects to be entitled under the contract.
Revenue recognition ASC 606 steps
5 step process of ASC 606
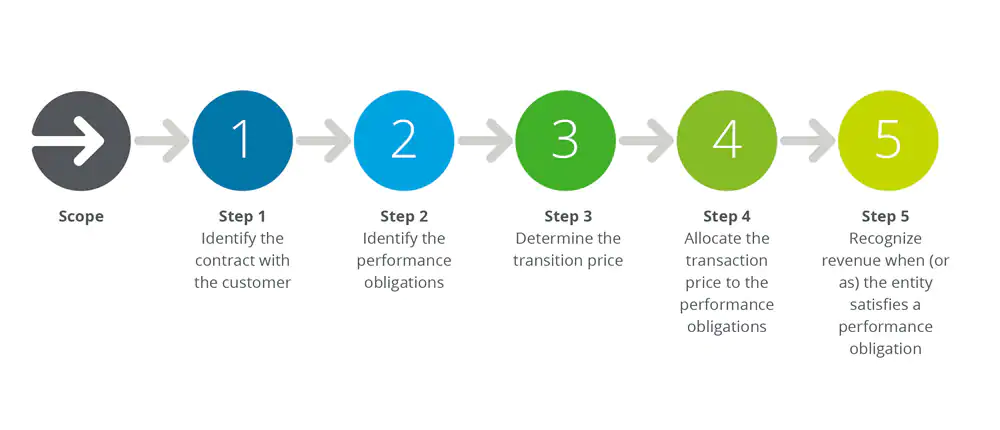
Foundry Bean Global Work System revenue steps for contracts.
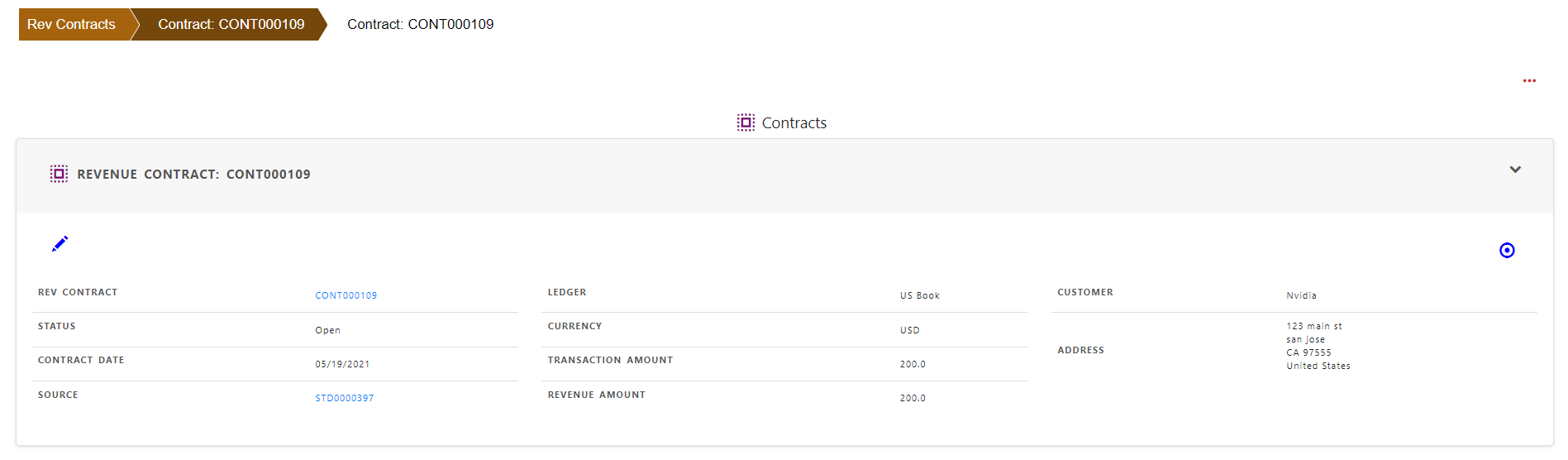
Step 1 : Itentify the contract with customer
Contract Number, contract date , customer name and address in Foundry Bean Contract Arrangement satisfy this requirement to identify the contract with customer.
Step 2 : Identify the performance obligations
The contract lines identify each and every performance obligations in the contract
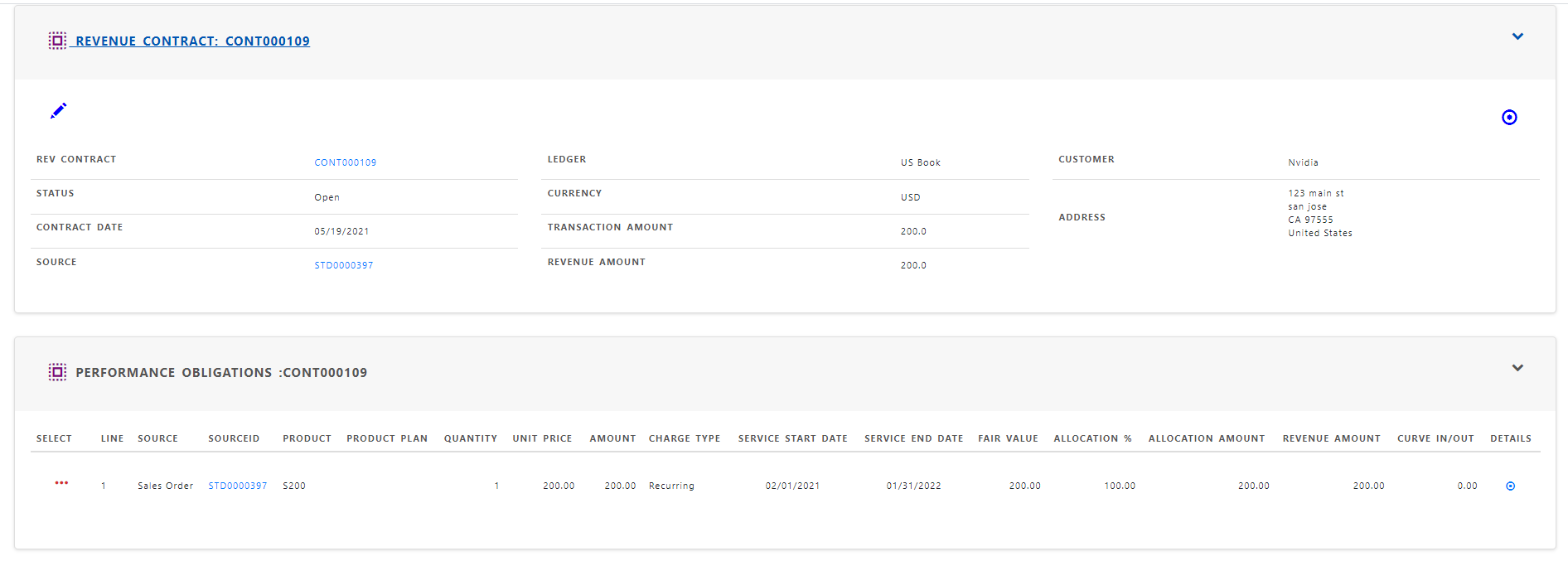
Step 3 : Determine the transaction price
Price, amount , charge type, service start date and service end date determine the transaction price for each performance obligation.
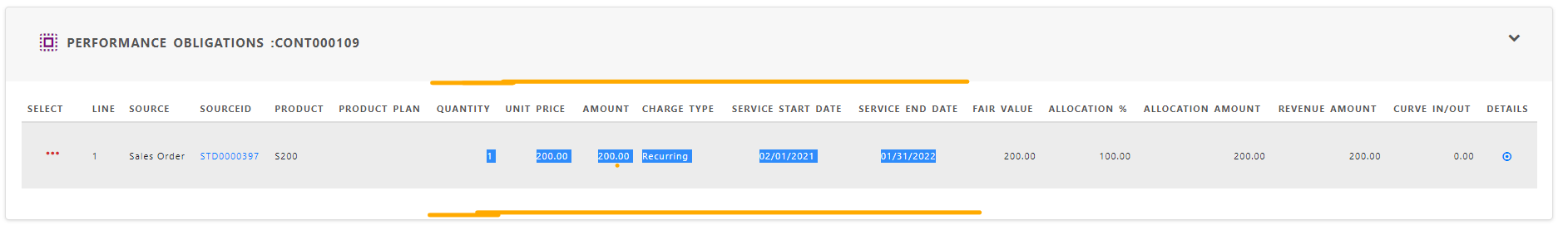
Step 4 : Allocate the transaction price
Fair Value , allocation % and allocation amount determine the allocated transaction price for each performance obligation.
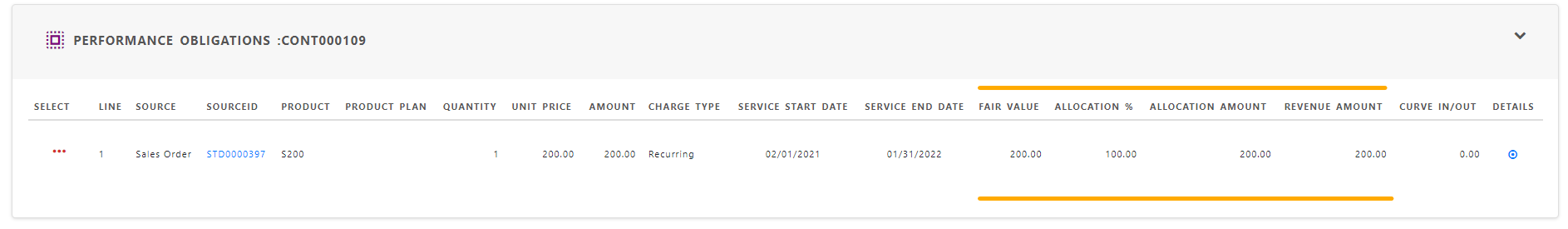
Step 5: Recognize revenue when (or as) the entity satisfies a performance obligation.
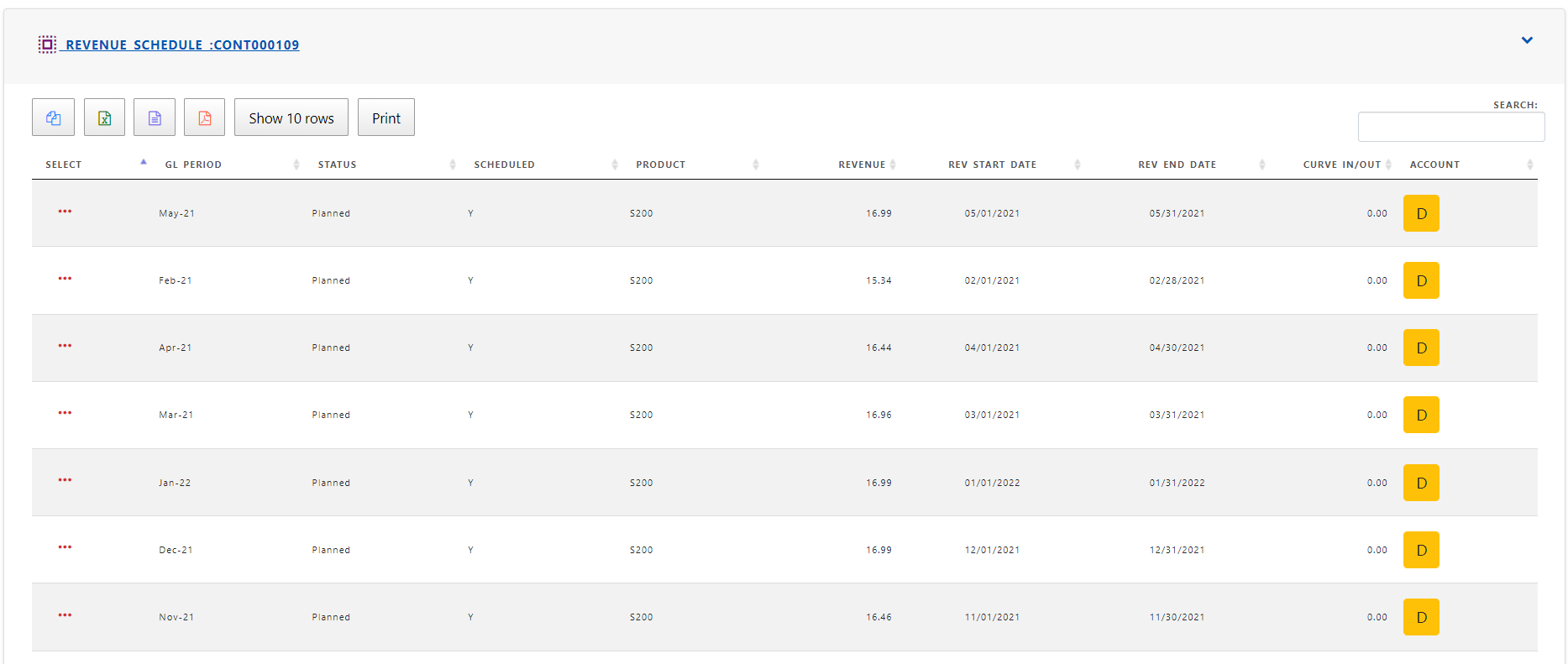
Revenue schedule created during service contract creation determine revenue to be recognized during an accounting period. By default schedules are planned and after revenue recognition of lines , the status chaged to “RevRec”.